2003 AMC 10A Problems/Problem 22
Problem
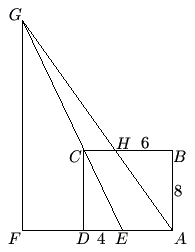
In rectangle ![]() , we have
, we have ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() is on
is on ![]() with
with ![]() ,
, ![]() is on
is on ![]() with
with ![]() , line
, line ![]() intersects line
intersects line ![]() at
at ![]() , and
, and ![]() is on line
is on line ![]() with
with ![]() . Find the length of
. Find the length of ![]() .
.
![]()
Solution
Solution 1
![]() (Opposite angles are equal).
(Opposite angles are equal).
![]() (Both are 90 degrees).
(Both are 90 degrees).
![]() (Alt. Interior Angles are congruent).
(Alt. Interior Angles are congruent).
Therefore ![]() and
and ![]() are similar.
are similar.
![]() and
and ![]() are also similar.
are also similar.
![]() is 9, therefore
is 9, therefore ![]() must equal 5. Similarly,
must equal 5. Similarly, ![]() must equal 3.
must equal 3.
Because ![]() and
and ![]() are similar, the ratio of
are similar, the ratio of ![]() and
and ![]() , must also hold true for
, must also hold true for ![]() and
and ![]() .
. ![]() , so
, so ![]() is
is ![]() of
of ![]() . By Pythagorean theorem,
. By Pythagorean theorem, ![]() .
.
![]() .
.
![]()
So ![]() .
.
![]() .
.
Therefore ![]() .
.
Solution 2
Since ![]() is a rectangle,
is a rectangle, ![]() .
.
Since ![]() is a rectangle and
is a rectangle and ![]() ,
, ![]() .
.
Since ![]() is a rectangle,
is a rectangle, ![]() .
.
So, ![]() is a transversal, and
is a transversal, and ![]() .
.
This is sufficient to prove that ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
Using ratios:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Since ![]() can't have 2 different lengths, both expressions for
can't have 2 different lengths, both expressions for ![]() must be equal.
must be equal.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Solution 3
Since ![]() is a rectangle,
is a rectangle, ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() . From the Pythagorean Theorem,
. From the Pythagorean Theorem, ![]() .
.
Lemma
Statement: ![]()
Proof: ![]() , obviously.
, obviously.
$\begin{eqnarray} \angle HCE=180^{\circ}-\angle CHG\\ \angle DCE=\angle CHG-90^{\circ}\\ \angle CEED=180-\angle CHG\\ \angle GEA=\angle GCH \end{eqnarray}$ (Error compiling LaTeX. Unknown error_msg)
Since two angles of the triangles are equal, the third angles must equal each other. Therefore, the triangles are similar.
Let ![]() .
.

Also, ![]() , therefore
, therefore
![]()
We can multiply both sides by ![]() to get that
to get that ![]() is twice of 10, or
is twice of 10, or ![]()
Solution 4
We extend BC such that it intersects GF at X. Since ABCD is a rectangle, it follows that CD=8, therefore, XF=8. Let GX=y. From the similarity of triangles GCH and GEA, we have the ratio 3:5 (as CH=9-6=3, and EA=9-4=5). GX and GF are the altitudes of GCH and GEA, respectively. Thus, y:y+8 = 3:5, from which we have y=12, thus GF=y+8=12+8=20. B.
See Also
| 2003 AMC 10A (Problems • Answer Key • Resources) | ||
| Preceded by Problem 21 |
Followed by Problem 23 | |
| 1 • 2 • 3 • 4 • 5 • 6 • 7 • 8 • 9 • 10 • 11 • 12 • 13 • 14 • 15 • 16 • 17 • 18 • 19 • 20 • 21 • 22 • 23 • 24 • 25 | ||
| All AMC 10 Problems and Solutions | ||